Derives value for the output calls from a neighborhood of
cells centered in the output cell. The neighborhood is with user defined
shape (square or circle) and size (width or diameter) in number of cells.
Neighborhoods:
Square - Width = 3

Square - Width = 5
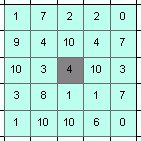
Circle - Diameter = 3
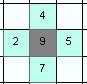
Circle - Diameter = 5
Inputs:
- Input raster dataset
- Output
raster name and format
- Neighborhood shape
- Neighborhood size (width for square and
diameter for circle) in pixels/number of cells. The size needs to be an odd
number in order to place the cell for which the calculations are performed
in the center of the neighborhood.
- Statistics
type .
- Integer and Floating point rasters
- Sum - the sum of the cell values within the
neighborhood
- Min - the minimum values within the
neighborhood
- Max - the maximum value within
the neighborhood
- Range - the range of values within the
neighborhood
- Mean - the average of the values within
the neighborhood
- STD - the standard deviation of the values in
the neighborhood
- Median - the median value in the
neighborhood
- Integer rasters only
- Major - the majority value (the value
that appears most times in the neighborhood).
- Minor - the minority value (the value
that appears least times in the neighborhood).
- Variety - variety (the number of unique
values in the neighborhood).
Output:
- A raster with type
depending on the type of the input raster and the type of statistics
performed.
- Floating point input raster - Floating point output
- Integer input raster
- MEAN or STD statistics type - Floating point output
- Any other type statistics - Integer output
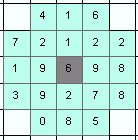
Example:
- Sum = 49
- Min = 2
- Max = 9
- Range = 7
- Mean = 5.44
- STD = 2.54
- Median = 5
- Major = 3
- Minor = 2
- Variety = 7
Notes:
- Supported raster formats are File Geodatabase raster, Personal Geodatabase
raster and file based raster formats (ESRI GRID, Erdas Imagine and
TIFF).
- For file based rasters initially the name of the output raster
defines the raster format
- no extension specified - ESRI binary GRID
- .img extension (for example raster1.img) -
ERDAS IMAGINE image.
- .tif extension (for example raster1.tif -
Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) image.
- The initial output raster format can be
changed by selecting the desired output in the dialog.
- The input raster must be in a projected
coordinate system.
ToolBox
implementation
Command line syntax
ETS_GPFocalStatistics <Input Raster> <Out
Raster> <Statistics Type> <Neighborhood Type> <Neighborhood Size>
Parameters
| Expression |
Explanation |
| <Input
Raster> |
A
Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| <Out
Raster> |
A String
- the full name of the output raster (A raster with the same full
name should not exist). The output raster type depends on the extension
of the output file(see Notes above) |
|
<Statistics Type> |
A String - the type of the
statistics to be calculated. Valid values
- Sum
- Min
- Max
- Range
- Mean
- STD
- Median
- Major
- Minor
- Variety
|
|
<Neighborhood Type> |
A String - the neighborhood
type. Valid values: Square and Circle |
|
<Neighborhood Size> |
An integer - the side of the square or
the diameter of the circle in pixels/number of cells. This should be an
odd number. |
Scripting syntax
ETS_GPFocalStatistics (Input
Raster, Out Raster, Statistics Type, Neighborhood Type, Neighborhood Size)
See the explanations above:
<> - required parameter
{} - optional parameter
.NET implementation
(Go to TOP)
FocalStatistics (inRasterDataset As IRasterDataset2,
sOutRaster As String, sStatsType As String,
sNeighborhoodType As String, iSize As Integer) As IRasterDataset2
| Copyright © Ianko Tchoukanski |





